Not to be confused with a 1983 album by the appropriately-named English post-punk band Sad Lovers and Giants, this anthology edited by Galina Krasskova comes from over a decade ago during a rich period of publishing for Asphodel Press. As such, many of the contributions in this paean to Loki and his family draw from that then extant wealth of material, and have previously appeared variously in Raven Kaldera’s Jotunbok, Krasskova’s own Exploring the Northern Tradition, Elizabeth Vongvisith’s devotional Trickster, My Beloved, and others.
Not to be confused with a 1983 album by the appropriately-named English post-punk band Sad Lovers and Giants, this anthology edited by Galina Krasskova comes from over a decade ago during a rich period of publishing for Asphodel Press. As such, many of the contributions in this paean to Loki and his family draw from that then extant wealth of material, and have previously appeared variously in Raven Kaldera’s Jotunbok, Krasskova’s own Exploring the Northern Tradition, Elizabeth Vongvisith’s devotional Trickster, My Beloved, and others.
Following a brief introduction from Krasskova, and as is often the way with such titles, Feeding the Flame begins with an exhaustive introduction to its subject matter, this time in the form of Hot Stuff: Working with Loki from Mordant Carnival. The first part of this contribution provides a thorough survey of many of Loki’s attributes and associations, not necessarily heavy on the details, but touching a lot of bases through its journey; including his relationships with various other beings. Carnival writes fluidly and confidently in an arch and self-aware manner, with, as the essay’s title prophesises, the occasional descent into fittingly Lokian-humour and wry asides: a deprecating mention of Loki’s Dick Dastardy moustache in his appearance on the Snaptun bellows stone, say, or a description of Baldr as the brightest, the best and deadest of the gods.
Carnival then moves on to the essay’s second part with an exploration of working with Loki in the here and now, something that is introduced as being potentially problematic given that it is drawn from personal experience, which, they admit, could all simply be a figment of the imagination. Carnival provides a broad ritual method for working with Loki, with various avenues for further exploration via sacrifice or possession, noting that this structure is preferable to simply swapping Loki’s name into an existing Wiccan or similar format that is heavy on the abjuration and banishing.
Other writers provide long-form considerations of Loki, with Sophie Oberlander’s Courting the Trickster and Sigrun Freyskona’s account of Loki as a childhood imaginary friend reminiscent of Rik Mayall’s Drop Dead Fred, but the remaining contributions are poetic ones. These works are by largely familiar names from within this circle of publishing, such as Silence Maestas, Elizabeth Vongvisith, Michaela Macha and Krasskova herself. Poetically, the most striking of these are a couple of pieces from Maestas who combines unfettered devotion for their subject with a deft poetic voice, particularly in an untitled work which opens memorably with the evocative line “I’d like to teach my fool tongue to dance.” The award for most thematically striking poem, though, goes to Vongvisith, whose Fulltrui is positively filthy with its depiction of Óðinn and Loki’s blood brotherhood as something profoundly carnal, describing them as two mating wildcats, with the latter impaled with the flesh of the former after a chase through the worlds.
Loki does not possess the wolf’s share of the content in Feeding the Flame and a significant portion of what follows in the discussion of his family centres on his Æsir wife, Sigyn. There are 70 pages devoted to Sigyn, substantially more than for Loki himself, and if, like this writer, you’ve never felt much of an affinity with her, that’s a lot to get through. As with other examples of Sigyn literature from Asphodel Press, this material is interesting considering that, in her, much has been made from so little in lore. Thus, some of the imagery presented here has slight if any direct correlation within the sagas, being seemingly built solely on mutually affirming UPG (Unverified Personal Gnosis). Krasskova introduces this surfeit of content with an essay presenting Sigyn as a child bride whose aegis is the healing of the inner child; a theme she later returns to in a received telling of Loki and Sigyn’s first meeting. Others consider Sigyn as a spirit of endurance and eventual victory, and there are several practical contributions, with Jason Freysson giving instructions for a ritual bath for use in Sigyn devotions and a recipe for her oil, while Krasskova and Fuensanta Arismendi both provide separate meditations for her.
One of the unique aspects of Feeding the Flame is that its brief allows material to be presented for figures who would otherwise receive little attention, in particular Loki and Sigyn’s two sons, who are here, as per Snorri Sturluson, referred to as Narvi and Vali. There are several poetic and prose pieces dedicated to the brothers separately and as a duo, making this surely one of the few places to find such material.
Loki’s equine son, Sleipnir, also gets a poem dedicated to him and then the rest of the book is rounded off with material, both poem and prose, dedicated to Loki’s other wife, Angrboða, and their children Fenrir, Hela and the World Serpent. As one might expect, this author finds this section to be the most engaging, with a strong, imagery-rich collection of poetry for Angrboða, with Kaldera’s Mother of Monsters and Seawalker’s Hag of the Ironwood being particularly notable. The Hela selection is equally strong with Dagian Russell memorably addressing Her as Lady of the Cool Damp Places and Mistress of Eternal Autumn, amongst other wonderful titles, while another piece from Kaldera, Darkness Out of Fire, has Hela addresses Loki directly, daughter to father.
The prose of Feeding the Flame is of a consistent quality, despite the variety of authors, and there are no pieces that grate or feel out of place. Poetry, as one would expect, is a different matter, with a variety of styles. There are the invocatory prayer-type pieces that one expects in a devotional such as this, more declamatory than an ode, whereas others, notably Maestas and Vongvisith. traffic in a far more considered poetic manner, their structures and choice of words feeling worked and finessed, informed by an awareness of the form.
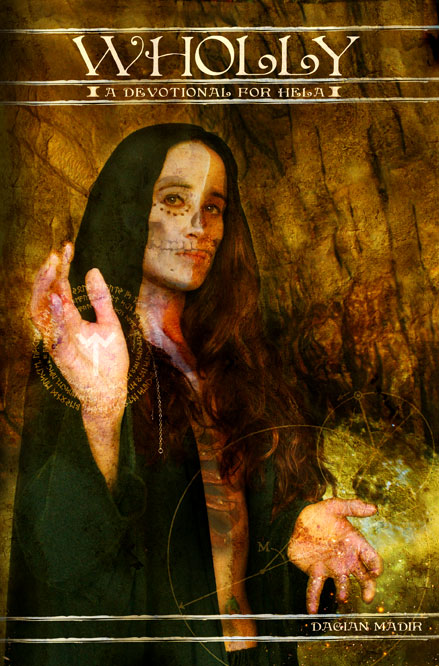
The layout of Feeding the Flame follows the standard in-house style of Asphodel Press, with a consistent serif for body and a different serif for titles. It’s nothing flash but it is consistent and clean; though I do wish first paragraphs weren’t indented, tsk. The book is devoid of internal illustrations but does bear as its cover depiction of Angrboða, Loki and Sigyn by Grace Palmer; and image which also appears as The Lovers trump in the Kaldera-compiled Giant’s Tarot.
While Feeding the Flame is still available in this Asphodel Press edition, Krasskova produced a reissue in 2014 retitled Consuming the Flames: A Devotional Anthology for Loki and His Family, with an Arthur Rackham cover, revised content, a reduced page count, and ironically, given the subtitle, a removal of all material dedicated to Angrboða, Hela, Fenrir and Jormungand. As such, the recommendation by necessity falls to the first edition, with the material for Loki’s most famous wife and children, though it is slight next to the voluminous and taxing devotions to Sigyn, being a particular selling point.
Published by Asphodel Press