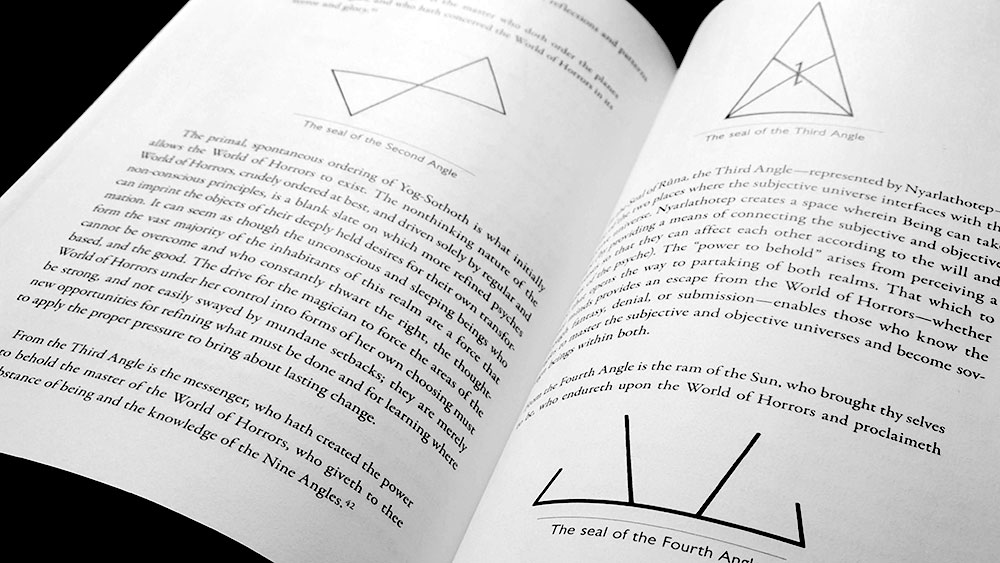
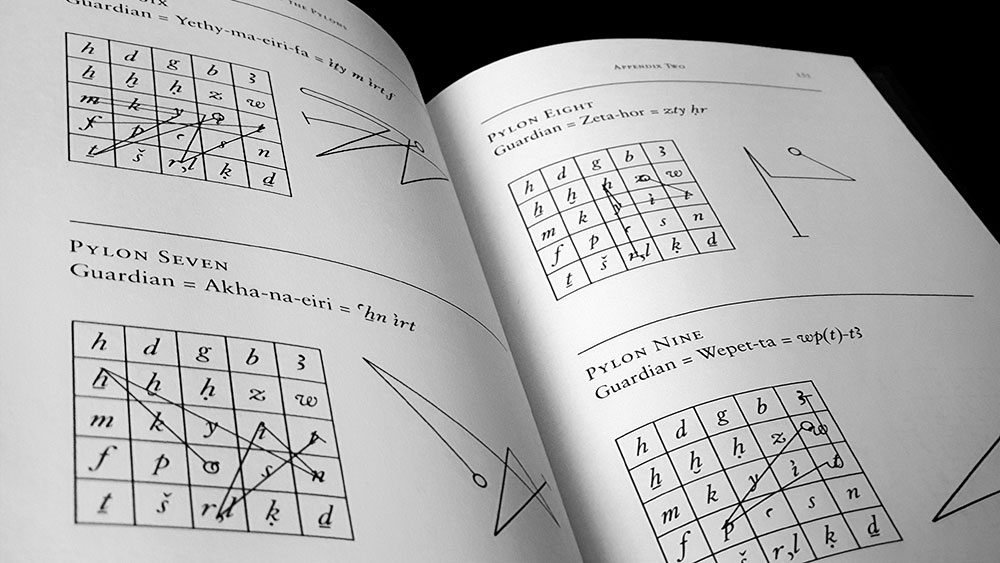
If you’re wondering what Henry Peacham’s Minerva Britanna is all about, a clue may, or may not, be found in the subtitle which describes it as “A Garden of Heroical Devices, Furnished and Adorned with Emblems and Impressas of Sundry Natures.” Minerva Britanna belongs to a category known as the emblem book in which allegorical illustrations (pictura) sit alongside a motto, usually in Latin (superscriptio), and an explanatory text ranging from a few lines of verse to pages of prose (subscriptio), creating complex patterns of often didactic signi?cation. The first emblem book, the sixteenth century Emblemata, first of its name, by Andrea Alciato, created a popular template and was followed by a raft of similar works over the following century, with Michael Maier’s Atalanta Fugiens being perhaps the most well-known of them. Peacham’s emblem book, published in 1612, 81 years after Alciato’s Emblemata, is reproduced in its entirety here, with little comment other than a several page introduction by Josephine McCarthy.
If you’re wondering what Henry Peacham’s Minerva Britanna is all about, a clue may, or may not, be found in the subtitle which describes it as “A Garden of Heroical Devices, Furnished and Adorned with Emblems and Impressas of Sundry Natures.” Minerva Britanna belongs to a category known as the emblem book in which allegorical illustrations (pictura) sit alongside a motto, usually in Latin (superscriptio), and an explanatory text ranging from a few lines of verse to pages of prose (subscriptio), creating complex patterns of often didactic signi?cation. The first emblem book, the sixteenth century Emblemata, first of its name, by Andrea Alciato, created a popular template and was followed by a raft of similar works over the following century, with Michael Maier’s Atalanta Fugiens being perhaps the most well-known of them. Peacham’s emblem book, published in 1612, 81 years after Alciato’s Emblemata, is reproduced in its entirety here, with little comment other than a several page introduction by Josephine McCarthy.
Peacham, in addition to being a draughtsman, player of tennis and falconer, could be described using the Artistotelian term graphice. Defined by Peacham himself in his Gentleman’s Exercise as someone who specialised in the “use of the pen in writing faire, drawing, painting, and the like,” it marked him as someone admirably able to execute both the written and illustrated aspects of Minerva Britanna. Consisting of 204 emblems, Minerva Britanna was an expansion on two earlier attempts at creating emblem books, one for King James and one for his son, both based on the king’s 1603 treatise on government Basilicon Doron. Though neither book was finished, 68 of the Basilicon Doron emblems found new life in the pages of Minerva Britanna.
McCarthy argues that whilst Minerva Britanna contains some elements of a Neoplatonist-type ascent, in which the soul aspires towards union with the ineffable, it is principally a text of faery magic, mixed with Elizabethan codes, Hermetic wisdom and kingly advice. For McCarthy, it is a book concerned with sacred kingship and its responsibilities, of the land and the sacred female power within it, something made clear with the title’s invocation of the goddesses Minerva and Britannia, matrons of wisdom and the land respectively. It is McCarthy’s contention that nineteenth century occultists, who have had an enduring influence on contemporary occultism, removed magic from the land, enclosing it in vaults and temples, and that the material in Minerva Britanna reflects a vision of magic truer to what was once common practice, one considerably more connected to the worlds of faery and the underworld. By using Minerva Britanna, practitioners are able to connect with this archaic strain of magic again, becoming reacquainted with the wildness, playfulness, puzzles and the shadow of the Faery Queene. Unfortunately, McCarthy doesn’t give any specific examples of emblems that may reflect this stream of faery magic or support her contention that Peacham was an initiate or at least a follower of its mysteries.
While this edition of Minerva Britanna is not presented as practical and complete workbook, McCarthy briefly offers several ways in which people can utilise Peacham’s emblems in magic. She suggests that the images can be used as a divination deck, divided into three main magical themes that facilitate connections with the sacred land, the faery realm and underworld prophecy. Following the book’s motto of Mente Videbor (‘by the mind I shall be seen’), McCarthy also describes using the emblems as persistent visual aids that then impinge on the subconscious in dreams or unexpected moments, sparking cathartic moments of recognition and realisation.
Although there are 204 emblems in Minerva Britanna they are by no means the sole creation of Peacham, denoting the derivative nature of the English strand of the emblem tradition as a whole. Eighty-four of the images draw from the works of such authors as Alciati himself, Theodore de Bèze, Joachim Camerarius, Camillo Camilli, Luca Contile, Paulo Giovio, Claude Paradin, Guillaume de La Perrière, Nikolaus Reusner, Cesare Ripa, Girolamo Ruscelli, Jacobus Typotius and Geoffrey Whitney, with fifteen based on Gerard de Jode’s engravings in Laurens van Haecht Goidtsenhoven’s Mikrokosmos = Parvvs mvndvs from 1579. Unlike de Jode’s fine engravings, Pencham’s emblems were rendered as woodcuts (following composition cues from Camerarius, Camilli, Ruscelli and Typotius), substantially removing the subtlety found in the images of Mikrokosmos, but adding a simplicity and immediacy.
Lest this seem like an accusation of plagiarism as we understand it today, Peacham acknowledges his debt to his antecedents in his introduction, telling the reader that he has “imitated the best approved Authors in this kind: as Alciat, Sambucus, Iunius, Reusneru, and others…”. Just as translation was seen as potentially creating a new work (and Peacham free translated Goidtsenhoven’s text for the emblems that draw from Mikrokosmos), Peacham was adhering to Renaissance ideals of imitation which were divided, in ascending order of worth, into sequi (‘following’), imitari (‘imitating’) and aemulari (‘emulating’). While sequi more closely mirrors our definition of plagiarism, the aemulari of Peacham aims to not only follow the original but to transform and surpass it. For an in-depth discussion of this theme, see Mason Tung’s From Theory to Practice: A Study of the Theoretical Bases of Peacham’s Emblematic Art (1997).
The imagery in Peacham’s emblems is as diverse as his inspirations, ornately framed and usually staged within the same seemingly eternal landscape found in similar alchemical and hermetic illustrations. The occupants of these archetypal vistas are often animals or human figures, though in others, heraldic elements come to the fore and weapons, armour, scrolls, crests and disembodied limbs float without context in the air. As one would expect, the book’s cast of characters is largely drawn from classical mythology and history, with Peacham acknowledging as his sources the Greek Anthology, the works of Horace, Ovid’s Metamorphoses, Pliny’s Natural History and Aesop’s Fables. There are also nods to figures contemporary with Peacham and a few moments that can be interpreted as being indebted to Edmund Spenser’s conception of fairyland in The Faerie Queene; such as the Shadie Wood of Una replicated in the Nulli penetrabilis emblem, with its “uncouth pathes, and hidden waies unknown… by banks of Acheron.” Spenser’s work has much of the emblem about it with its layers of allegory and rhetoric, as well as the poet’s ability to succinctly describe scenes and characters in a comparable manner. Despite this minor intersection between Peacham and Spenser, and other than the Arcadian gloss that is sometimes given to visions of the fae, there is little amongst the imagery of Minerva Britanna that seems obviously faery.
The subscriptio that follow each picture, consistently presented as two verses ending in a couplet, creates a verbal interplay with the preceding iconic elements. Whether the interplay is integrative or diversive, the two elements are intended to work as one, strengthening each other, with the ‘moral’ then being drawn in the final couplet or lines, like a punchline or the last line of a proto-meme.
It is worth noting that Minerva Britanna is in the public domain and several complete, high resolution scans are available on archive.org. While McCarthy’s introduction makes for interesting reading, its brevity does not make it indispensable, and so the real value of this edition is for those who want printed versions of the work, rather than a PDF. The emblems here have been digitally restored for reprinting by Michael Sheppard who performs an admirable job, removing the background texture of the original manuscript but leaving the lines clear and sharp, and unmarred by too much contrast. This edition of Minerva Britanna mirrors the original’s dedication to King James’ son Henry, the Prince of Wales, with a dedication to the current holder of that title who is described as “HRH Charles, Prince of Wales, Duke of Cornwall, Duke of Rothesay, King in Waiting, and beloved of the Faery Queene.”
Published by Quareia Publishing